Understanding "Not Retained": A Comprehensive Guide To Data Privacy, Legal Implications, And Best Practices
In today's digital age, the term "not retained" has become increasingly important in discussions around data privacy, legal compliance, and information management. As businesses and organizations collect vast amounts of data, understanding what "not retained" means and its implications is crucial for maintaining trust with users and complying with regulations.
The concept of "not retained" refers to the practice of not storing or keeping certain types of data after a specific period or under certain conditions. This practice is essential in ensuring compliance with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). By implementing "not retained" policies, organizations can protect sensitive information and reduce the risk of data breaches.
In this article, we will explore the meaning of "not retained," its significance in data management, and how it affects businesses and individuals. We will also discuss best practices for implementing "not retained" policies and provide insights into the legal and ethical considerations surrounding this topic.
- Infowars Reporter Murdered In Texas Unveiling The Shocking Truth
- Jake Tapper Challenges Gop Senator On Musk A Deep Dive Into The Controversial Debate
- Why Was Us Airman Shot Unveiling The Truth Behind The Incident
- Federal Layoffs Tarlovs Tense Clash
- Festival Chaos Attendee Bites Deputy
Table of Contents
- What Does "Not Retained" Mean?
- The Importance of "Not Retained" in Data Privacy
- Legal Frameworks and Regulations
- Benefits of Implementing "Not Retained" Policies
- Challenges in Enforcing "Not Retained" Practices
- Best Practices for "Not Retained" Implementation
- Impact on Businesses and Consumers
- Case Studies: Successful "Not Retained" Strategies
- Future Trends in Data Retention and Privacy
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What Does "Not Retained" Mean?
At its core, "not retained" refers to the deliberate decision not to store or keep certain data after it has served its purpose or after a predefined period. This practice is particularly relevant in industries that handle sensitive information, such as healthcare, finance, and e-commerce. By choosing not to retain data, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
For example, when a customer places an order on an online platform, their payment information may be processed and used for the transaction but not stored for future use unless explicitly consented to by the user. This approach aligns with the principles of data minimization and privacy by design, which are key components of modern data protection frameworks.
Key Characteristics of "Not Retained" Practices
- Data is deleted or anonymized after a specific period.
- User consent is obtained before retaining any personal information.
- Transparent policies are in place to inform users about data handling practices.
The Importance of "Not Retained" in Data Privacy
Data privacy has become a top priority for individuals and organizations alike. With the increasing frequency of data breaches and cyberattacks, protecting sensitive information is more critical than ever. The "not retained" approach plays a vital role in enhancing data privacy by limiting the amount of data that is stored and potentially exposed to unauthorized access.
- Tragic Murdersuicide Mom Finds Bodies Ndash A Heartbreaking Story
- Raiders Urgently Need Wr Talent A Comprehensive Analysis
- Khalil Mack Joins Chargers A Gamechanging Move For The Nfl
- Try The Trump Sandwich At Canadian Cafe A Unique Culinary Experience
- Moscow Hit By Massive Drone Attack A Comprehensive Analysis
Moreover, implementing "not retained" practices demonstrates an organization's commitment to safeguarding user information and respecting their privacy rights. This can enhance trust and loyalty among customers, leading to improved brand reputation and customer retention.
How "Not Retained" Aligns with Privacy Principles
- Data Minimization: Only collect and retain the minimum amount of data necessary for a specific purpose.
- Purpose Limitation: Use data only for the purposes for which it was collected.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate data handling practices to users.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations
Several legal frameworks and regulations mandate the implementation of "not retained" practices to ensure compliance with data protection standards. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, for instance, requires organizations to delete personal data when it is no longer necessary for the purposes for which it was collected. Similarly, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) grants consumers the right to request the deletion of their personal information.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal consequences. Organizations must therefore prioritize the development and enforcement of "not retained" policies to avoid potential penalties and protect user data.
Key Regulations Supporting "Not Retained" Practices
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Benefits of Implementing "Not Retained" Policies
Implementing "not retained" policies offers numerous benefits for both organizations and individuals. For businesses, these policies reduce the risk of data breaches, lower storage costs, and enhance compliance with regulatory requirements. For consumers, "not retained" practices ensure greater privacy and control over their personal information.
Additionally, organizations that adopt "not retained" practices can improve their reputation and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace by demonstrating a strong commitment to data privacy and security.
Top Benefits of "Not Retained" Policies
- Reduced risk of data breaches
- Lower storage and management costs
- Improved compliance with legal requirements
- Enhanced trust and customer loyalty
Challenges in Enforcing "Not Retained" Practices
While the benefits of "not retained" practices are clear, implementing these policies can pose several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is ensuring that all departments within an organization adhere to the same data retention standards. This requires clear communication, training, and the development of robust data management systems.
Another challenge is balancing the need for data retention with the demands of business operations. Some organizations may require certain data to be retained for auditing, reporting, or legal purposes, making it essential to establish clear guidelines and exceptions to "not retained" policies.
Addressing Common Challenges
- Develop comprehensive data retention policies.
- Provide regular training and education for employees.
- Implement automated data deletion processes.
Best Practices for "Not Retained" Implementation
To successfully implement "not retained" practices, organizations should follow a set of best practices that ensure compliance, efficiency, and effectiveness. These practices include conducting regular data audits, establishing clear retention schedules, and leveraging technology to automate data deletion processes.
Additionally, organizations should prioritize transparency and communication with users, ensuring that they are informed about data handling practices and their rights regarding data retention and deletion.
Essential Best Practices
- Conduct regular data audits to identify unnecessary data.
- Establish clear retention schedules based on legal and operational needs.
- Automate data deletion processes to ensure consistency.
- Communicate transparently with users about data handling practices.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The implementation of "not retained" practices has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers. For businesses, these practices can lead to improved compliance, reduced costs, and enhanced reputation. For consumers, "not retained" policies provide greater peace of mind and control over their personal information.
However, the success of "not retained" practices depends on the willingness and ability of organizations to adopt and enforce these policies effectively. By prioritizing data privacy and security, organizations can create a win-win situation for both themselves and their customers.
Key Impacts on Businesses and Consumers
- Improved compliance and reduced legal risks for businesses.
- Enhanced trust and loyalty among consumers.
- Increased control over personal information for users.
Case Studies: Successful "Not Retained" Strategies
Several organizations have successfully implemented "not retained" strategies, demonstrating the effectiveness of these practices in enhancing data privacy and compliance. For example, a major e-commerce platform adopted a policy of automatically deleting user payment information after a transaction is completed, reducing the risk of data breaches and improving customer trust.
Similarly, a healthcare provider implemented a system for anonymizing patient data after a specific period, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations while maintaining the quality of care. These case studies highlight the importance of tailoring "not retained" practices to the unique needs and requirements of each organization.
Lessons from Successful Implementations
- Tailor "not retained" policies to organizational needs.
- Leverage technology to automate data deletion processes.
- Engage stakeholders in the development and enforcement of policies.
Future Trends in Data Retention and Privacy
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the practices and regulations surrounding data retention and privacy. Emerging trends such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will likely influence how organizations approach "not retained" practices in the future.
Additionally, the increasing focus on data sovereignty and cross-border data transfer regulations will require organizations to adapt their "not retained" strategies to meet global standards and protect user information effectively.
Key Trends to Watch
- Advancements in data anonymization techniques.
- Growing emphasis on data sovereignty and localization.
- Increased use of blockchain for secure data management.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding and implementing "not retained" practices is essential for organizations seeking to enhance data privacy, ensure compliance with regulations, and build trust with consumers. By adopting best practices, addressing challenges, and staying informed about emerging trends, organizations can successfully navigate the complexities of data retention and privacy in today's digital landscape.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with "not retained" practices in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into data privacy, security, and compliance. Together, we can create a safer and more transparent digital environment for everyone.
- Pope Francis Predicts Short Papacy A Comprehensive Analysis
- Uk Crossbow Killer Gets Life Sentence A Comprehensive Analysis
- Patriots Land Pro Bowl Wr Deal Revolutionizing The Nfl Offensive Strategy
- Barkley Criticizes Canadians On Gretzky A Comprehensive Analysis
- Mariners Demote 2024 Reliever To Triplea A Comprehensive Analysis
What Does "Not Retained" Mean After Applying for a Job? Salarship
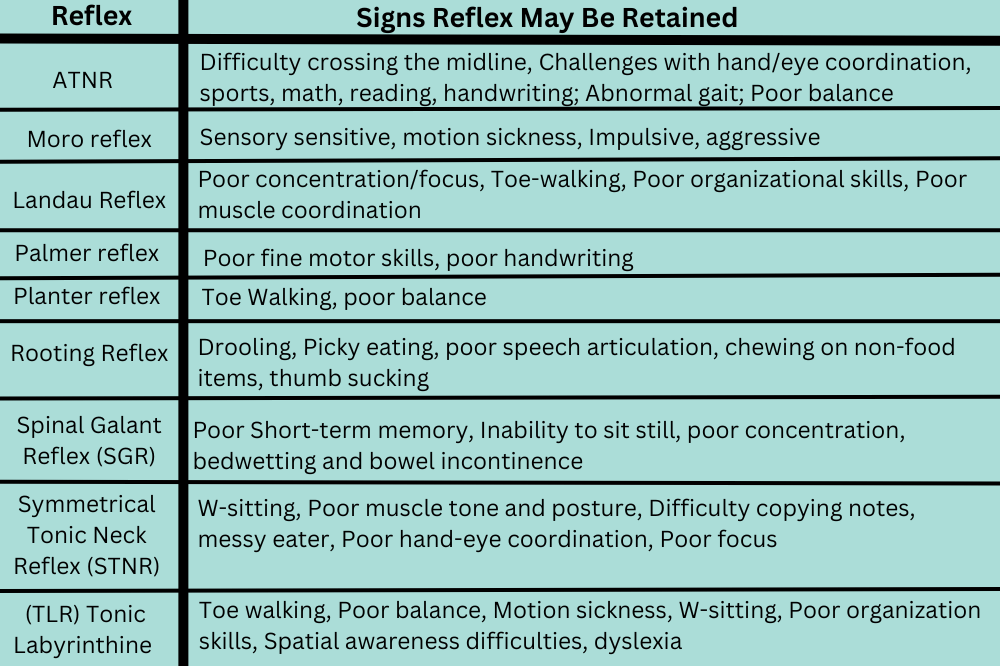
Retained Primitive Reflexes As A Sign Of Brain Imbalance, 48 OFF

Retained Earnings Important Terms, Concepts, and Calculation Explained