Melting Point Of Copper: A Comprehensive Guide
Copper is one of the most widely used metals in the world due to its excellent conductivity and malleability. The melting point of copper plays a crucial role in determining its suitability for various applications. Understanding this property is essential for engineers, scientists, and manufacturers alike.
From ancient civilizations to modern industries, copper has been a cornerstone of technological advancement. Its melting point is a fundamental property that influences its behavior under heat and its ability to be molded into different forms. This article will explore the melting point of copper, its significance, and how it affects industrial processes.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the science behind the melting point of copper, its applications, and the factors that influence it. Whether you're a student, researcher, or professional, this article will provide valuable insights into this critical material property.
- Russia Advances 100 Km In Kursk A Comprehensive Analysis Of The Military Operations
- Band Booed Faces Online Trolls A Deep Dive Into The Realities Of Music Criticism In The Digital Age
- Education Chief Mcmahon Cuts Bureaucracy Transforming The Educational Landscape
- Pedro Jimeno Dating Sophie Sierra Everything You Need To Know About Their Relationship
- Moms Tragic Role In Babys Death A Heartbreaking Story And Lessons Learned
Table of Contents
- What is Melting Point?
- Melting Point of Copper
- Factors Affecting Melting Point
- Applications of Copper
- Copper Alloys and Their Melting Points
- History of Copper Usage
- Scientific Explanation of Copper's Melting Point
- Industrial Significance of Copper's Melting Point
- Environmental Impact of Copper Melting
- Future Research Directions
What is Melting Point?
The melting point refers to the temperature at which a solid substance transitions into a liquid state at standard atmospheric pressure. This physical property is crucial for understanding material behavior and designing processes that involve heating or cooling. For metals like copper, the melting point determines their suitability for high-temperature applications.
Importance of Melting Point in Metallurgy
In metallurgy, the melting point is a key parameter that affects material selection for specific applications. It influences how metals are processed, cast, and formed into desired shapes. Understanding this property is essential for ensuring the durability and performance of metallic components under varying conditions.
Melting Point of Copper
Copper has a melting point of approximately 1,085°C (1,985°F). This relatively high temperature makes copper suitable for applications that require resistance to heat, such as electrical wiring, plumbing, and heat exchangers. The melting point of copper is a result of its atomic structure and metallic bonding, which we will explore further in later sections.
- Trumps Doj Fights Mass Firings A Deep Dive Into The Legal And Political Battle
- Ny Banker Charged With Rape A Comprehensive Analysis
- Donnarummas Heroics Secure Psg Victory
- Jackie Kennedys Controversial Diet Revealed
- Brownsrsquo New Qb Acquisition Unveiled A Gamechanging Move
Measurement Techniques
The melting point of copper can be measured using various techniques, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermal analysis. These methods provide precise data on the temperature at which copper transitions from a solid to a liquid state. Accurate measurement is critical for quality control in industrial processes.
Factors Affecting Melting Point
Several factors can influence the melting point of copper, including impurities, pressure, and alloy composition. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing the performance of copper in different applications.
- Impurities: The presence of impurities in copper can lower its melting point. Pure copper has a higher melting point compared to copper with impurities.
- Pressure: Increasing pressure can raise the melting point of copper. This effect is significant in high-pressure industrial processes.
- Alloy Composition: Adding other metals to copper to form alloys can alter its melting point. For example, brass, a copper-zinc alloy, has a lower melting point than pure copper.
Applications of Copper
Copper's high melting point, combined with its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, makes it ideal for a wide range of applications. Some of the most common uses of copper include:
- Electrical wiring
- Plumbing systems
- Heat exchangers
- Jewelry and decorative items
- Coins and currency
Role in Renewable Energy
Copper plays a vital role in renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines. Its high melting point ensures durability and reliability in high-temperature environments, making it an essential material for sustainable energy solutions.
Copper Alloys and Their Melting Points
Copper alloys, such as brass and bronze, have different melting points depending on their composition. These alloys are widely used in various industries due to their unique properties. Below is a table summarizing the melting points of common copper alloys:
| Alloy | Composition | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Brass | Copper + Zinc | 900 - 1,000 |
| Bronze | Copper + Tin | 950 - 1,050 |
| Gunmetal | Copper + Tin + Zinc | 1,000 - 1,100 |
History of Copper Usage
Copper has been used by humans for over 10,000 years. Its discovery marked the beginning of the Copper Age, a period of significant technological advancement. The melting point of copper was one of the first properties to be exploited by ancient civilizations, enabling them to create tools, weapons, and ornaments.
Modern Applications
In modern times, copper continues to be a critical material in industries ranging from electronics to construction. Its melting point remains a key factor in determining its suitability for various applications, from wiring in computers to pipes in plumbing systems.
Scientific Explanation of Copper's Melting Point
The melting point of copper is determined by its atomic structure and metallic bonding. Copper atoms are arranged in a face-centered cubic lattice, which provides strong metallic bonds between the atoms. These bonds require a significant amount of energy to break, resulting in a high melting point.
Thermodynamics of Melting
From a thermodynamic perspective, the melting point of copper represents the temperature at which the Gibbs free energy of the solid and liquid phases are equal. At this point, the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium, allowing copper to transition smoothly from one state to another.
Industrial Significance of Copper's Melting Point
In industrial processes, the melting point of copper is a critical parameter for designing furnaces, casting molds, and other equipment. Ensuring that copper remains stable at high temperatures is essential for maintaining the integrity of components and systems.
Challenges in High-Temperature Applications
While copper's high melting point makes it suitable for high-temperature applications, it also presents challenges. For example, maintaining the purity of copper during melting and casting requires careful control of process conditions to prevent oxidation and contamination.
Environmental Impact of Copper Melting
The melting and processing of copper can have significant environmental impacts, including energy consumption and emissions. Efforts to reduce these impacts include developing more efficient melting processes and recycling copper to conserve resources.
Sustainable Practices
Recycling copper not only reduces the need for mining but also lowers the energy required to produce new copper products. This approach aligns with global efforts to promote sustainability and reduce the carbon footprint of industrial activities.
Future Research Directions
Research into the melting point of copper and its alloys continues to focus on improving material properties and developing new applications. Areas of interest include:
- Enhancing thermal stability
- Developing advanced alloys with tailored melting points
- Exploring new processing techniques
Innovative Applications
As technology advances, copper's melting point may enable new applications in fields such as aerospace, electronics, and nanotechnology. Continued research will help unlock the full potential of this versatile material.
Conclusion
The melting point of copper is a fundamental property that influences its behavior and suitability for various applications. From ancient civilizations to modern industries, copper's high melting point has made it an indispensable material. Understanding this property is essential for engineers, scientists, and manufacturers seeking to optimize the performance of copper in different contexts.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. For more informative articles on materials science and engineering, explore our website and stay updated on the latest developments in the field.
- Zuckerbergs Surprising Favorite President A Deep Dive Into His Political Views
- Fbi Sting Reveals Political Bribery Unveiling The Depths Of Corruption
- Ice Targets Green Card Holders What You Need To Know
- Doge Declared Black Box Secret Unveiling The Cryptocurrency Enigma
- Trump Halts Affordable Housing Projects A Comprehensive Analysis

Melting Copper
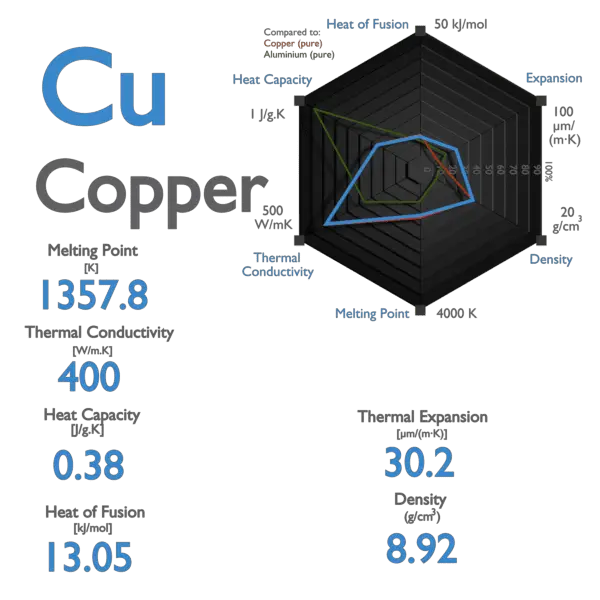
Copper Melting Point Boiling Point
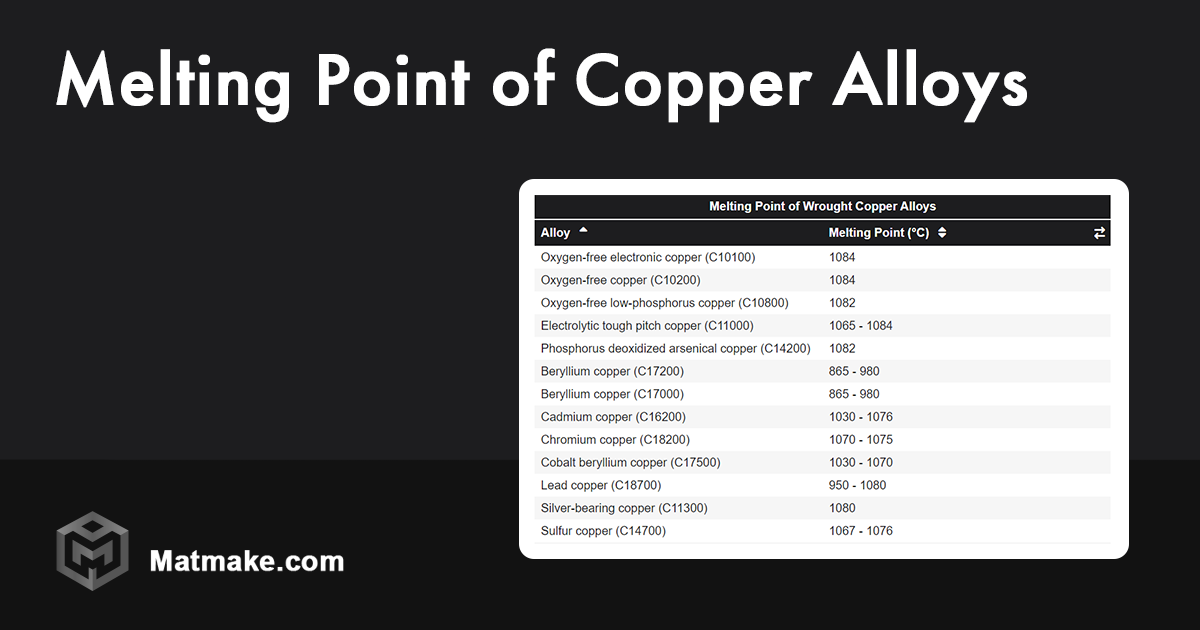
Melting Point of Copper Alloys Table