How Many Languages In India: A Comprehensive Guide To India's Linguistic Diversity
India is a country renowned for its incredible cultural and linguistic diversity. The question of how many languages in India often sparks curiosity among linguists, travelers, and global citizens alike. With a population exceeding 1.4 billion, India boasts one of the most complex linguistic landscapes in the world. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of India's languages, their significance, and the factors contributing to their diversity.
India's linguistic richness is not just a reflection of its history but also a testament to its vibrant present. The Constitution of India recognizes multiple languages, making it a unique example of multilingualism in action. Understanding the linguistic landscape of India helps us appreciate the cultural depth and heritage of this remarkable nation.
In this article, we will delve into the complexities of India's languages, explore their origins, and discuss their importance in modern society. Whether you're a language enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about India's cultural fabric, this guide will offer valuable insights into the nation's linguistic diversity.
- Infowars Reporter Murdered In Texas Unveiling The Shocking Truth
- Chris Matthews On Trade War We Will Lose
- Jasmine Pinedas Shocking Survival Story A Tale Of Resilience And Courage
- Trump Trade War Hits Retirement Accounts The Impact On Your Financial Future
- Hairstylist Charged After Teen Payment Scuffle A Comprehensive Analysis
Table of Contents
- How Many Languages in India
- Official Languages of India
- Regional Languages in India
- Minority Languages in India
- Language Families in India
- India's Language Policy
- Census Data on Languages in India
- Efforts to Preserve Indigenous Languages
- The Role of Languages in Indian Culture
- Conclusion
How Many Languages in India?
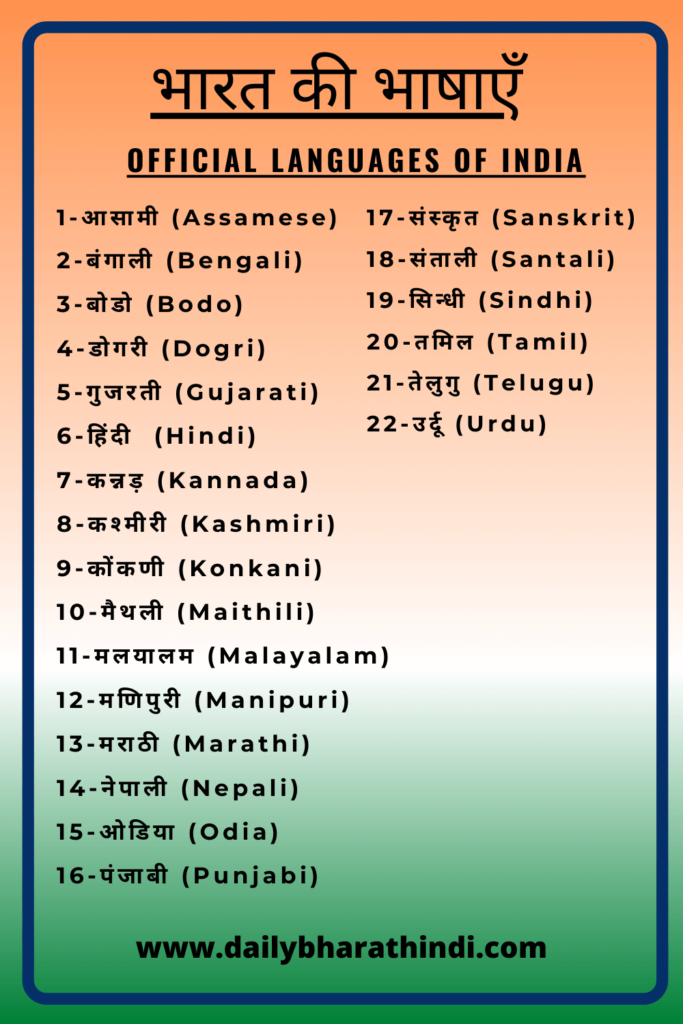
India is home to an astonishing number of languages. According to the People's Linguistic Survey of India (PLSI), there are over 780 languages spoken in the country. However, the official Census of India recognizes only 122 languages, which include 22 scheduled languages under the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution. The discrepancy arises from the criteria used to classify a dialect as a distinct language.
The linguistic diversity in India is unparalleled, with languages belonging to four major language families: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Austroasiatic, and Tibeto-Burman. This diversity is a result of centuries of cultural interactions, migrations, and historical influences.
Factors Contributing to Linguistic Diversity
- Geographical diversity
- Cultural exchanges over centuries
- Influence of foreign invaders and traders
- Migration patterns within the country
Official Languages of India
The Constitution of India designates two official languages for communication at the national level: Hindi and English. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is the primary official language, while English serves as a subsidiary official language for administrative purposes.
- Trump Tariffs Seen As Tax Cut A Comprehensive Analysis
- Donnarummas Heroics Secure Psg Victory
- Ruth Marcus Quits Over Bezos Column A Detailed Analysis Of The Resignation And Its Implications
- Harvey Weinsteins Showbiz Secrets Leaked Unveiling The Hidden Truths
- Pattinson Praises Zendaya For Calming Role A Comprehensive Exploration
It is important to note that the use of Hindi as the sole official language has been a topic of debate in India. Many states, especially in the southern part of the country, prefer to use regional languages for official communication.
Regional Languages in India
India's states and union territories have their own official languages, reflecting the linguistic preferences of their populations. For example:
- Tamil is the official language of Tamil Nadu.
- Malayalam is spoken predominantly in Kerala.
- Bengali is the official language of West Bengal.
These regional languages play a crucial role in preserving the cultural identity of their respective regions. The diversity of regional languages contributes to India's rich cultural tapestry.
Minority Languages in India
Besides the major languages, India is home to numerous minority languages spoken by smaller communities. Some of these languages are on the verge of extinction due to globalization and urbanization. Examples of such languages include:
- Konkani
- Manipuri
- Sindhi
Efforts are being made to document and preserve these languages to ensure they are not lost to future generations.
Challenges Faced by Minority Languages
Minority languages face challenges such as:
- Limited educational resources
- Declining number of speakers
- Urban migration leading to language shift
Language Families in India
India's languages belong to four major language families:
- Indo-Aryan: Includes Hindi, Bengali, Punjabi, and Urdu.
- Dravidian: Includes Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam.
- Austroasiatic: Includes languages like Santali and Ho.
- Tibeto-Burman: Includes languages like Bodo and Manipuri.
Each language family has its own unique characteristics and historical roots, contributing to the linguistic diversity of India.
India's Language Policy
India's language policy is enshrined in its Constitution, which recognizes the importance of linguistic diversity. The Eighth Schedule of the Constitution lists 22 scheduled languages, providing them with official status and support for development. The policy aims to promote multilingualism while ensuring that no language is marginalized.
Education plays a critical role in language policy, with schools encouraged to teach in the mother tongue or regional language. This approach helps preserve linguistic heritage and ensures that students can learn effectively in a familiar language.
Census Data on Languages in India
The Census of India provides valuable insights into the linguistic makeup of the country. According to the 2011 Census:
- Hindi is the most spoken language, with over 528 million speakers.
- English is widely used as a second language, especially in urban areas.
- Other major languages include Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, and Tamil.
Data from the census helps policymakers understand the linguistic needs of the population and plan accordingly.
Importance of Census Data
Census data on languages is crucial for:
- Planning educational programs
- Designing communication strategies
- Preserving endangered languages
Efforts to Preserve Indigenous Languages
Preserving indigenous languages is a priority for linguists and cultural organizations in India. Initiatives such as the People's Linguistic Survey of India (PLSI) aim to document and promote lesser-known languages. Educational institutions are also incorporating indigenous languages into their curricula to encourage their use.
Technology plays a significant role in language preservation, with digital platforms and apps being developed to teach and promote endangered languages. These efforts ensure that India's linguistic heritage is not lost to future generations.
The Role of Languages in Indian Culture
Languages are an integral part of Indian culture, influencing art, literature, music, and cinema. Each language carries its own unique traditions and customs, contributing to the rich cultural diversity of the country. For example:
- Tamil literature dates back over 2,000 years, showcasing the depth of the language.
- Bollywood films often incorporate multiple languages, reflecting the multilingual nature of Indian society.
- Folk music and dances are performed in regional languages, preserving cultural heritage.
The interplay of languages in Indian culture highlights the importance of linguistic diversity in shaping the nation's identity.
Conclusion
India's linguistic diversity is a source of pride and strength for the nation. The question of how many languages in India reveals a complex and fascinating landscape shaped by history, geography, and culture. From the official languages of Hindi and English to the numerous regional and minority languages, India's linguistic heritage is a treasure worth preserving.
We encourage readers to explore the languages of India further and appreciate their significance in shaping the nation's identity. Share your thoughts in the comments below, and don't forget to explore other articles on our site to learn more about India's rich cultural tapestry.
Sources:
- People's Linguistic Survey of India
- Census of India
- Constitution of India
- Goldman Sachs Downgrades Us Economy What It Means For You
- Ivanka Trump Returns To Politics Exploring Her Potential Political Comeback
- Raiders Acquire Fast Expacker A Gamechanging Move For The Nfl Season
- Nba Not Ready For Shai Amp Kd Duo The Ultimate Powerhouse
- Cowboys Sign Topranked Local Star A Gamechanging Move For The Franchise

Exploring India’s Linguistic Diversity How Many Languages Are Spoken

Languages in India How Many are There?
Languages In India