Student Loan Repayment Rules Revealed: A Comprehensive Guide
Student loan repayment can be a daunting task for many graduates, but understanding the rules can make the process more manageable. The burden of student loans has become a significant financial concern for millions of individuals worldwide. As education costs continue to rise, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the repayment rules and strategies to ensure you are prepared for the financial commitment ahead.
Whether you are a recent graduate or someone who has been managing student loans for years, this article aims to provide valuable insights into the repayment process. By understanding the regulations, options, and strategies available, you can create a repayment plan that works best for your financial situation.
In this guide, we will explore the ins and outs of student loan repayment rules, including federal and private loan options, income-driven repayment plans, loan forgiveness programs, and more. Let's dive into the details so you can take control of your financial future.
- Mark Jackson Criticizes Unnamed Player A Comprehensive Analysis
- New Poll Hits Trump Hard A Comprehensive Analysis
- Tragic Murdersuicide Mom Finds Bodies Ndash A Heartbreaking Story
- Exsecondround Pick Joins Raiders A Gamechanging Move For The Franchise
- Earthquakes Threaten Us Volcano Eruption Understanding The Growing Risk
Table of Contents
- Understanding Student Loan Basics
- Types of Student Loans
- Repayment Options and Plans
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans
- Loan Forgiveness Programs
- Deferment and Forbearance Options
- Loan Consolidation and Refinancing
- Tax Implications of Student Loan Repayment
- Preventing Loan Default
- Tips for Managing Student Loans
Understanding Student Loan Basics
Before diving into the repayment rules, it's important to understand the basics of student loans. Student loans are financial tools designed to help students pay for education-related expenses, including tuition, books, and living expenses. These loans can come from various sources, such as the government or private lenders.
There are two main types of student loans: federal and private. Federal student loans are funded by the U.S. Department of Education and come with certain protections and benefits, such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs. Private student loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions, and often lack the same level of flexibility.
Understanding the differences between these loan types is crucial in determining the best repayment strategy. By familiarizing yourself with the terms and conditions of your loans, you can make informed decisions about how to manage your debt effectively.
- Moscows Largest Drone Strike Before Talks A Comprehensive Analysis
- Kaitlan Collins Clashes Over Ceo Assassin Website A Deep Dive Into The Controversy
- Khalil Mack Joins Chargers A Gamechanging Move For The Nfl
- Rubio Ukraine Needs Talks Not War Ndash A Comprehensive Analysis
- Trump Trade War Hits Retirement Accounts The Impact On Your Financial Future
Types of Student Loans
Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans are provided by the government and come with various benefits, such as fixed interest rates and flexible repayment options. Some common types of federal student loans include:
- Direct Subsidized Loans: Available to undergraduate students with financial need.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans: Available to undergraduate and graduate students without requiring a demonstration of financial need.
- Direct PLUS Loans: Offered to graduate students and parents of dependent undergraduates to help cover education expenses.
Private Student Loans
Private student loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. These loans typically have variable interest rates and fewer repayment options compared to federal loans. Borrowers should carefully consider the terms and conditions before opting for a private loan.
It's essential to weigh the pros and cons of both federal and private loans to determine which option aligns best with your financial goals and needs.
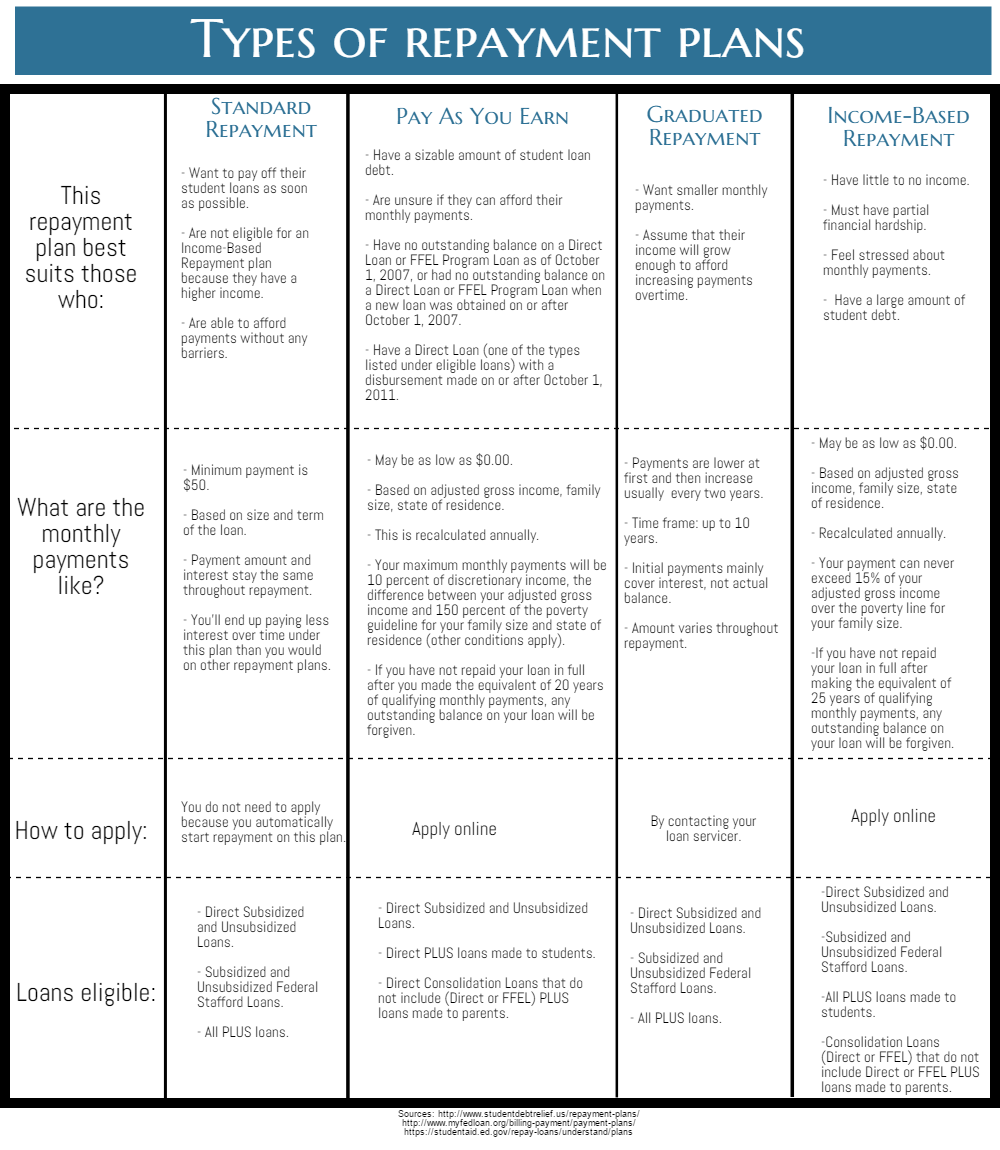
Repayment Options and Plans
Once you graduate or leave school, you will need to start repaying your student loans. The standard repayment plan typically lasts for 10 years, but there are other options available depending on your financial situation.
Here are some of the most common repayment plans:
- Standard Repayment Plan: Fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: Payments start lower and increase every two years, typically over a 10-year period.
- Extended Repayment Plan: Extended repayment period of up to 25 years, available for loans exceeding $30,000.
Choosing the right repayment plan depends on your income, debt level, and long-term financial goals. It's important to evaluate your options carefully to find the plan that best suits your needs.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
What Are Income-Driven Repayment Plans?
Income-driven repayment (IDR) plans are designed to make student loan payments more affordable by adjusting them based on your income and family size. These plans typically extend the repayment period to 20 or 25 years and offer the possibility of loan forgiveness after that time.
Types of Income-Driven Repayment Plans
There are several IDR plans available, each with its own eligibility requirements and benefits:
- Income-Based Repayment (IBR): Limits monthly payments to 10% or 15% of discretionary income, depending on when you borrowed.
- Pay As You Earn (PAYE): Caps payments at 10% of discretionary income for new borrowers after October 1, 2007.
- Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE): Available to all borrowers, capping payments at 10% of discretionary income.
Income-driven repayment plans can be a lifeline for borrowers struggling to manage their student loan debt. By aligning payments with your income, these plans can help reduce the financial burden and make repayment more manageable.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
Loan forgiveness programs are designed to provide relief to borrowers who meet specific criteria, such as working in public service or teaching in underserved areas. Some of the most popular forgiveness programs include:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): Forgives remaining loan balances after 120 qualifying payments for borrowers working in public service jobs.
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness: Offers up to $17,500 in loan forgiveness for teachers working in low-income schools or educational service agencies.
- Income-Driven Repayment Forgiveness: Forgives remaining balances after 20 or 25 years of payments under an IDR plan.
While loan forgiveness programs can provide significant relief, they often come with strict eligibility requirements. It's important to research and understand the terms of these programs to determine if you qualify.
Deferment and Forbearance Options
What Is Deferment?
Deferment allows you to temporarily pause or reduce your student loan payments under certain circumstances, such as returning to school, serving in the military, or experiencing economic hardship. During deferment, interest on subsidized loans is paid by the government, while unsubsidized loans continue to accrue interest.
What Is Forbearance?
Forbearance is another option for temporarily stopping or reducing payments, but it is generally used when deferment is not available. Unlike deferment, interest continues to accrue on both subsidized and unsubsidized loans during forbearance.
Both deferment and forbearance can provide short-term relief, but they should be used cautiously as they can increase the overall cost of your loans due to accruing interest.
Loan Consolidation and Refinancing
Loan consolidation and refinancing are strategies that can simplify your repayment process and potentially lower your interest rates. Federal loan consolidation combines multiple federal loans into a single loan with a fixed interest rate based on the weighted average of the original loans.
Private loan refinancing, on the other hand, involves taking out a new loan with a private lender to pay off existing loans. This can result in lower interest rates and more favorable terms, but you may lose access to federal loan benefits such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs.
Before pursuing consolidation or refinancing, it's important to weigh the pros and cons and ensure that it aligns with your long-term financial goals.
Tax Implications of Student Loan Repayment
Student loan interest may be tax-deductible, providing some relief for borrowers. The Student Loan Interest Deduction allows you to deduct up to $2,500 of interest paid on qualified student loans each year, subject to certain income limitations.
Additionally, if you qualify for loan forgiveness programs, it's important to be aware of potential tax consequences. For example, forgiven debt under income-driven repayment plans may be considered taxable income, while PSLF forgiveness is generally tax-free.
Consulting with a tax professional can help you navigate the tax implications of student loan repayment and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Preventing Loan Default
Defaulting on student loans can have severe consequences, including damaged credit, wage garnishment, and loss of eligibility for federal benefits. To avoid default, it's crucial to stay informed about your repayment obligations and take proactive steps if you encounter financial difficulties.
Some strategies to prevent default include:
- Contacting your loan servicer to discuss available options, such as deferment, forbearance, or income-driven repayment plans.
- Maintaining open communication with your lender and staying up-to-date with account information.
- Exploring loan consolidation or refinancing to lower monthly payments and improve financial flexibility.
By taking these steps, you can protect your financial well-being and avoid the negative consequences of default.
Tips for Managing Student Loans
Managing student loans effectively requires a combination of planning, discipline, and informed decision-making. Here are some tips to help you navigate the repayment process:
- Create a budget that accounts for your student loan payments and other financial obligations.
- Prioritize paying off high-interest loans first to reduce the overall cost of debt.
- Take advantage of automatic payment programs to ensure timely payments and potentially reduce interest rates.
- Stay informed about changes in student loan regulations and explore new opportunities for relief or forgiveness.
By following these tips, you can take control of your student loan debt and work toward achieving financial stability.
Kesimpulan
Student loan repayment can be a complex and challenging process, but by understanding the rules and available options, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. From choosing the right repayment plan to exploring loan forgiveness programs, there are many strategies to help you manage your debt effectively.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into personal finance and student loan management. Together, we can work toward a brighter financial future for all.
- Prince William Discusses Harry Meeting A Royal Insight Into Reconciliation And Family Ties
- Trumps Doj Fights Mass Firings A Deep Dive Into The Legal And Political Battle
- Bears Secure Top Pass Rusher A Deep Dive Into The Impactful Signing
- Elon Musk Criticizes Amtrak Usage A Comprehensive Analysis
- Evan Engrams Broncos Update The Latest On His Impact Career And Future With The Team
Student loan repayment options

Fillable Online Student Loan Repayment Rules Fax Email Print pdfFiller
Student Loan Repayment Calculator Template in Excel, Google Sheets